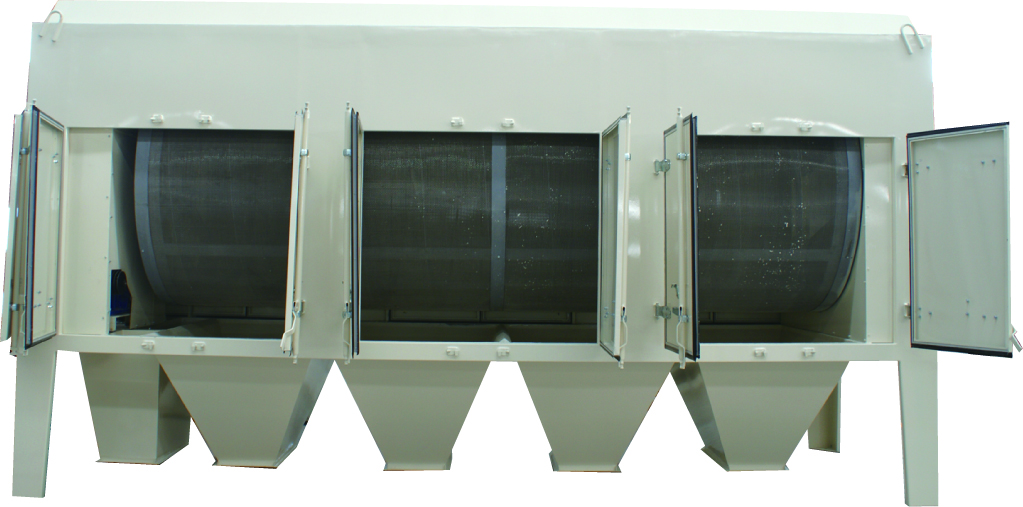
Drum
type pre cleaner is the main and primary machine in
high capacity grain cleaning industry. Drum type pre cleaner is used to remove
big, small impurity from grain seeds. At the meantime, drum type pre cleaner removes
the light impurity by connecting air dust cleaning system. Base on the
different cleaning aim, drum pre cleaner can be single drum sieve or double drum sieves. So the big straw, long
branches, sands, smashed seeds, dust, etc all can be removed by drum type
pre cleaner. Precleaner is fit for
all type grain seed cleaning, as maize, soya bean, wheat, oat, etc. Its
cleaning capacity ranges from 20-200 ton per hour. Base on different raw
material, different capacity requirement, we will suggest suitable sieves.
Drum type pre cleaner is driven by gear motor
and adopts chain transmission. This construction ensures its stable working
performance. There is a sieve brush equipped and brush the rotation sieves.
This effectively prevents grain seed clogging in sieve holes. Drum pre cleaner has a full-closed cover. This avoids dust leakage during operation and protects
working environment. On top of the pre
cleaner, there is an opening to connect the air suction system. At bottom
of drum type pre cleaner are the impurity and clean outlets. So drum pre cleaner is always placed on a platform or a higher frame to collect the
finished grain.
With good cleaning effect and user friendly
feature, pre cleaning machine is widely used in heavy duty Grain Cleaning Plant,
as grain supply center, big farm, seeds company.
Outer
sieve (mm)
Inner sieve (mm)
dia: 1.8-3.2
dia: 22
dia: 20
dia: 18
dia: 16
5XZP85/190D
60 tons/hour
50 tons/hour
40 tons/hour
30 tons/hour
5XZP100/220D
80 tons/hour
70 tons/hour
60 tons/hour
50 tons/hour
5XZP8100/320D
110 tons/hour
100 tons/hour
90 tons/hour
70 tons/hour
5XZP100/420D
140 tons/hour
120 tons/hour
110 tons/hour
100 tons/hour
5XZP125/320D
140 tons/hour
120 tons/hour
100 tons/hour
90 tons/hour
5XZP125/420D
170 tons/hour
150 tons/hour
120 tons/hour
110 tons/hour
Drum Type Pre-Cleaner,Rice Cleaning Machine,Grain Cleaning Machine,Wheat Cleaning Machine SHIJIAZHUANG SYNMEC INTERNATIONAL TRADING LIMITED , http://www.seedgraincleaner.com
Local breed chicken sheds
Local chicken breeds in China are very rich in resources. Most of them are both meat and egg-type varieties. They have the characteristics of resistance to roughage, wide adaptability, strong foraging ability, strong resistance, strong resistance to disease, good body appearance and excellent meat quality. Both are suitable for rearing techniques in greenhouses. The technology is briefly introduced as follows. 1 Construction of Sheds 1.1 Site Selection for Chicken Sheds Sheds for local chickens can be built in hilly areas, orchards or in woods. The site selection should take into account the area of ​​the chicken shed and the topography of the location of the chicken shed. There must be a sporting area around the chicken shed. The hens and weeds are the best places for chickens. It is therefore advisable to build sheds on the grassy slopes. The construction of a chicken shed should be on a high-dry, flat or slightly sloped mountain, and drainage is easy. The topography of the ground in the shed is slightly higher than the topography around the shed so as to facilitate drainage within the shed, which is conducive to the drying of the floor inside the shed. The chicken shed is located north to the south and toward the southeast, with favorable ventilation, sunshine and drainage. Should not be built in the day and night temperature difference is too big peak and poorly ventilated low-lying land. When selecting a site, factors such as the quality of the water source, traffic and electricity, and whether or not there is a pollution source around the site should be considered. 1.2 The structure of chicken sheds The chicken sheds can be built according to local conditions. Local materials are used because they are simple. At the same time, ventilation, lighting and Other factors must be taken into account. Feeding operations should also be considered. It is necessary to consider insulation and cold, but also to consider cooling. The framework of chicken shelters can be supported by bamboo. The roof height is 2~2.5m, the edge of the shed is 1.5~2.0m high, the top frame is herringbone, the roof is covered with oil felt, straw curtain, plastic sheet, etc., surrounded by plastic sheet and linoleum , and so on, but we must consider the hot summer weather cooling problem. The surrounding materials can be used for activities, and can be dismantled at any time, especially for sheds where chicks are raised. It is necessary to consider the heat insulation as well as the ventilation and ventilation and the humidity in the shed. In the summer, vines such as loofah, beans, and pumpkins can be grown on both sides of the greenhouse for shade and cooling. Around the greenhouse can also be built into a 1 ~ 1.2m high brick wall, surrounded by a plastic film, the south wall of the brick wall to leave a few can close the hole for chickens into and out of the greenhouse. The film on both sides of the greenhouse (southern and north sides) can be lifted by 0.8 to 1.0 m in hot weather to allow the wind to pass through the sides to facilitate cooling. There must be a drainage ditch around the greenhouse so that rain can be drained away in time when it rains, so as to prevent the water outside the shed from affecting the ground in the shed. The size of the greenhouse area should be determined according to the number of chickens, but it is appropriate to use 800-1000 feathers per shed. 2 Feeding and management during brooding period According to the growth and development rules of local chickens and the characteristics of feeding and management, the feeding cycle can be divided into brooding period (0 to 6 weeks old), breeding period (7 to 16 weeks old) and laying period (17). ~22 weeks old) Three phases. 2.1 Preparation of Brooders Before brooding to raise chickens, brooding must be done. This is the key to the success or failure of local chickens. Because chicks are small and delicate, they have poor adaptability and are very sensitive to environmental conditions. Therefore, brooding is a very careful and important work. In order to enable the chicks to grow normally and create the most suitable environmental conditions, the preparatory work for each brood must be completed. First you need to prepare a brooding house. Brooders require good insulation and ventilation. Before brooding, the brooding house must be rinsed clean and strictly sterilized. A disinfection pool should be prepared at the entrance of the brooding house. Work shoes and work clothes should be replaced when entering the house. Second, we must prepare brooding equipment and equipment. The equipment and equipment used are: First, heating equipment. Electricity, coal, charcoal and other heat sources, insulation equipment commonly used electric insulation umbrella, infrared light, coal stove or charcoal furnace. The second is the lighting. In the brooding room and under the umbrella, a lamp should be installed so that the chicks are close to the heat source and can easily feed and drink, and can be closed after one week. The third is the thermometer. It is used to detect the temperature inside the indoor and incubator, and according to different brooding methods to select the position detection that can represent the indoor temperature. The fourth is the trough. The food trough is required to be smooth and smooth, the chicks are easy to feed, and no feed is wasted, and the washing and disinfection are convenient at the same time. The fifth is a drinking fountain. Commonly used drinking fountains include bucket-type drinking fountains, bell-type vacuum drinking fountains, sink-type drinking fountains, and the like. Chicken farmers can use glass canned bottles and flat plates to form drinking fountains, and also can use bamboo and household utensils to make drinking fountains. All brooding utensils should be rinsed and disinfected. Once again, we must prepare feed, litter and drugs, and vaccines. The feed should be formulated according to the feeding standards of the chicks, and can be used for self-provisioned or purchased special-purpose feeds. Grass mats require dryness, softness, good water absorption, cleanliness, and no mildew. Sawdust and chaff are commonly used. Also prepare preventive drugs and vaccines and disinfectants. In addition, the brooding house should be preheated before brooding, and the temperature should be warmed up 1-2 days before the brooding, so that the temperature of the brooding house gradually rises to the required temperature for the chicks. If the heat source is coal or charcoal, check the temperature. Whether the flue or chimney leaks, it is found that the smoke should be plugged in time to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning in chicks. 2.2 Feeding of young chicks 2.2.1 Feeding: The first feeding of hatched chicks is said to be eating. It is an important part of raising young chicks. Feed the chicks as soon as possible, especially if they can eat feeds with added medications to improve the survival of chicks. One of the important measures of the rate. The morning and evening of eating will directly affect the appetite, digestion and growth of the chicks, so it is necessary to choose the right time to eat. Usually within 12 to 24 hours after the chicks hatch, the chickens can stand and walk, and about one-third of the chicks can eat when they have a search performance. The food that is eaten requires fresh, high quality, moderate grain size, easy to feed, nutritious, and easily digestible, commonly used broken rice or broken corn as a starter. Start with a small amount of feed evenly sprinkled on small trays or newspapers or dark plastic sheets, allowing them to feed freely. After 2 to 3 days after eating, feed should be fed with compound feed, which requires good quality, good palatability, and high quality. Feeding should be done with less feeding and more meals. The design of the food trough should be reasonable, so that chickens can freely feed and prevent the chicks from wasting and contaminating the feed by crawling into the trough. 2.2.2 Feed: Chicks have a small stomach capacity and metabolism is very strong. In order to meet the needs of the growth and development of chicks, it is required that the diet of the chicks is rich in nutrients, comprehensive and good quality, fresh, diversified, good palatability, easy to digest, avoid feeding large feed, feed with a large amount of crude fiber content. The general requirements for the nutritional level of the chick diet are: metabolic energy 11.9 ~ 12.1MJ/kg, crude protein is 18% ~ 20%, with special attention to vitamin and mineral content. 2.2.3 Drinking water: The initial drinking time of the newborn chicks can be taken at the same time as the start of eating but before the start of drinking, the drinking water cannot be cut off after drinking, and sufficient fresh clean drinking water should be provided. Drink water to use a dedicated drinking fountains, the number should be adequate, distribution in the brooding room should be uniform. The height of the drinking fountain should be adjusted in time with the growing age of chicks. The drinking fountain should be cleaned and disinfected regularly to prevent the contamination of feces. Water temperature at 15 ~ 20 °C, in the chicks first drinking water, per liter of water plus glucose 50g and vitamin C1g. Before the start of eating, each chick dropped 2 to 3 drops of cod liver oil and oxytetracycline mixture. 3 to 5 days after shelling, add 1000 IU of gentamycin and penicillin to drinking water or add some other antibiotics such as enrofloxacin solution. 2.3 Management of chicks 2.3.1 Proper temperature: This is an important condition for brooding and it is the key to brooding. The optimum temperature for brooding is: 33 to 35°C in the first week (refers to the temperature in the warming umbrella). As the age increases, the temperature can gradually decrease. It decreases by 2°C every week from the second week, and usually it is 30 to 40 days. Age off. The warming-off time should be flexibly controlled according to different seasons. During the cold season, the dewarming time should be delayed. During the hot season, the temperature can be defrosted in advance. The brooding temperature should be kept as stable as possible and should never be higher or lower. Whether the temperature is suitable or not can be judged according to the dynamics of the flock. 2.3.2 Appropriate Relative Humidity: The degree of humidity, although not as stringent as temperature, can also cause harm to chicks under certain conditions or when combined with other factors. When the humidity is too low, the feathers grow poorly, the skin is dry, the dust in the air is flying, and respiratory diseases are easily induced. When the humidity is too high, conditions are created for the reproduction of germs and eggs, which can easily cause chicken disease. The appropriate relative humidity is 65% to 70% in the first week, and 55% to 60% in the second week. 2.3.3 Fresh air: chickens grow fast, have strong metabolism, fast breathing, high body temperature, combined with intensive feeding, breathing carbon dioxide, excrement, and contaminated harmful gases emitted by the grass, polluting the air and causing poor growth and development of chicks. Because of this, it is necessary to pay attention to ventilation and keep the air in the house fresh. 2.3.4 Correct illumination: Light affects the chick's intake, drinking, exercise, and health. Light can promote chicks to feed on drinking water, improve chick viability, but also increase the body's vitamin D, promote calcium and phosphorus balance. Therefore, artificial lighting should be supplemented when the natural lighting time is insufficient. 2.3.5 Reasonable Density: The size of the rearing density should be based on reasonable arrangement of chicken species, shed structure, ventilation and management conditions, and seasonal conditions. Generally suitable density is: 1 to 15 days of age 30 to 40 per square meter, 16 to 28 days of age 20 to 30 per square meter, 29 to 42 days of age 15 to 20 per square meter, after 43 days of age 10/m2. 2.3.6 Strict health and epidemic prevention system: The chicks are small in size, weak in disease resistance and intensively reared. Once an outbreak occurs, it is difficult to control, especially in greenhouses, and the conditions are poor. Therefore, during the brooding period, the work of sanitation and epidemic prevention must be effectively carried out, and attention should be paid to environmental sanitation, strict disinfection and isolation systems. The use of drugs should be done regularly for the prevention of bacillus leukaemia and coccidiosis. Vaccination should also be done according to immunization procedures. In addition, during the brooding period, you must also observe and find problems in a timely manner. 3 Rearing and management of the rearing period After the chicks have entered the breeding period, the plumage of the chickens has become full, the digestive function has been improved, the feed intake has been greatly increased, the activity is lively, the growth and development are extremely fast, and the growth of bones, muscles and organs is in a prosperous period. . There are two purposes for rearing broilers: one is to cultivate an excellent rearing group of breeding chickens; the other is to make them reach the weight of commercial chickens as soon as possible and put them on the market for sale. Therefore, the quality of broiler rearing and management is directly related to whether it can be cultivated into a healthy chicken breeder group with high production capacity and breeding value. It is of vital importance whether the chicken can be slaughtered regularly and the production efficiency is in good order. 3.1 Breeding of broiler chickens The broiler chickens used for seedling maintenance must adopt limited, limited quality, and limited time-limited feeding methods so as to maintain the proper weight of the chickens and start production at a proper time, so as to increase the weight of eggs laid and increase the production of eggs. The breeding hens should be fed low-energy, low-protein cereals and bran feeds from the age of 8 weeks. However, from the 20th week of age, the nutrients level should be increased to lay a good foundation for laying eggs. Broiler chickens sold as commodity chickens should adopt free-feeding feeding methods, preferably using high-protein full-fed feeds, and the nutrient levels are generally 11.9 to 12.1 MJ/kg for metabolic energy, and 18% to 18.5% for crude protein. . 3.2 Management of broiler chickens The optimum temperature for broiler chickens is 15 to 20°C. In summer when the temperature is high, artificial cooling measures should be used to reduce the rearing density; in cold winters, cold insulation work should be done. Suitable relative humidity for broilers is 50% to 55%. In the rainy season, measures should be taken to reduce the humidity, keep the house dry, change the litter, clean the manure in time, and prevent the water from overflowing from the water dispenser. Light during the breeding period directly affects sexual maturity. In order to improve the egg production performance and egg quality of breeders, the age of sexual maturity should be appropriately delayed. Therefore, the light period in the rearing period can only be gradually shortened and must not be gradually increased. In the growing process of broiler chickens, there is a phenomenon of non-uniformity in size. Roosters grow faster than hens. Therefore, chickens must be reared in groups according to their size, strength, and size. The weak chicks should be kept alone, strengthened management, and carefully fed so that the overall chicken population can grow evenly. Breeding chickens grow fast, and in order to ensure that the house is clean and air fresh, and to prevent the development of lice and development is not neat, must adjust the feeding density according to the chicken's growth and development process. The use of reserved chickens can increase the amount of exercise properly, while commodity chickens need to control exercise, reduce consumption, and fatten the market as soon as possible. In order to prevent the spread of infectious diseases and to facilitate the thorough disinfection of poultry houses and utensils, an all-in, all-out feeding system must be adopted. Chickens of different batches and ages cannot be kept in two chicken sheds (two batches). There must be a period of free time. 4 Epidemic and disease prevention procedures 4.1 Suggested immunization procedures 4 to 5 days old kidney type chicken infectious bronchitis oil emulsion inactivated vaccine, 0.25 ml per chicken intramuscular injection; 7 to 9 days old chicken Newcastle disease IV series vaccine + transmission H120 dual vaccine Eyedrops, nasal drops once (or at the same time each chicken neck subcutaneous injection of 0.2ml chicken Newcastle disease oil emulsion inactivated vaccine); 14 to 16 days of infectious cystic disease poisoning vaccine dose of drinking water or infectious cysts lyophilized attenuated vaccine Double the amount of drinking water; 26 to 28 days of infectious cyst poisoning vaccine double the amount of drinking water; 31 to 33 days of age Newcastle disease IV vaccine double dose of water (such as 7 to 9 days have been injected Newcastle disease oil seedlings can be exempted from this item). 4.2 It is recommended to use oral rehydration salts for 1 day of age and 14 to fill water immediately; 2 to 6 days of age to eliminate drinking water, 2 times a day, and gentamicin 40,000 IU/L for drinking; 8 to 12 days old Vegetarian powder 0.005% to 0.01% drinking water; 15 to 17 days of norfloxacin pure powder 0.005% drinking water; 15 days after the use of a variety of anticoccidial drugs (such as Maduramycin, chlorpheniramine, salinomycin, etc. ) Alternately, use the drug for 7 days to stop for 5 days; 31 to 33 days of age, cyproteine ​​or enrofloxacin 0.005% drinking water.